금속 가공 시 공구 마크의 원인과 해결 방법
Precision metal parts are often manufactured using various precision machining technologies, with CNC machining being a common method. Usually, precision parts typically demand high standards for both dimensions and appearance.
Therefore, when using CNC machining metals such as aluminum and copper, the occurrence of tool marks and lines on the finished product’s surface is a concern. This article discusses the reasons that cause tool marks and lines during the machining of metal products. We also propose potential solutions.

Insufficient Clamping Force of Fixtures
Causes: Some cavity metal products need to use vacuum fixtures, and may struggle to generate sufficient suction due to the presence of surface irregularities, resulting in tool marks or lines.
Solution: To mitigate this, consider transitioning from simple vacuum suction to vacuum suction combined with pressure or lateral support. Alternatively, explore alternative fixture options based on specific part structures, tailoring the solution to the particular problem.

Process-related Factors
Causes: Certain product manufacturing processes may contribute to the issue. For instance, products like tablet PC rear shells undergo a sequence of machining steps involving punching side holes followed by CNC milling of the edges. This sequence can lead to noticeable tool marks when milling reaches the side-hole positions.
Solution: A common instance of this problem occurs when the aluminum alloy is chosen for electronic product shells. To resolve it, the process can be modified by replacing the side hole punching plus milling with only CNC milling. At the same time, ensuring consistent tool engagement and reducing uneven cutting when milling.
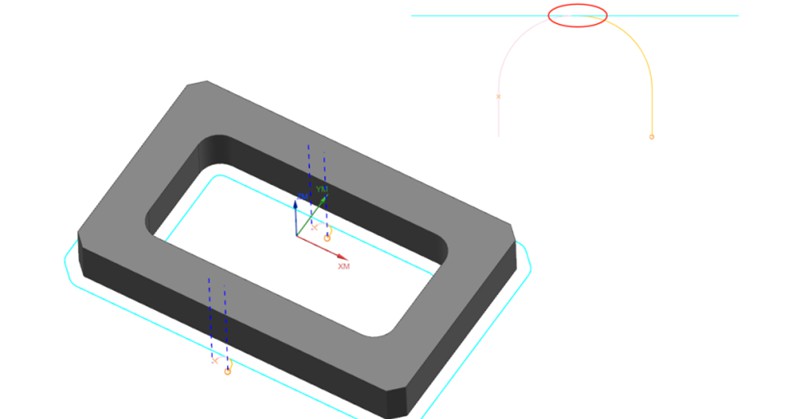
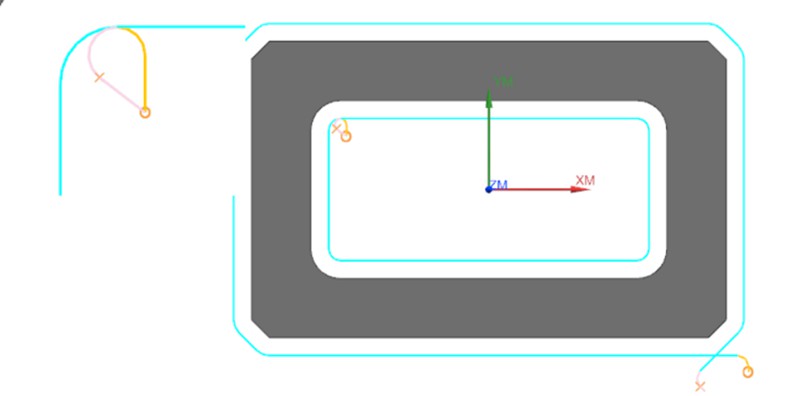
Inadequate Programming of Tool Path Engagement
Causes: This issue commonly arises during the 2D contour machining phase of product production. Poorly designed tool path engagement in the CNC program, leaving traces at the entry and exit points of the tool.
Solution: To address the challenge of avoiding tool marks at entry and exit points, a typical approach involves introducing a slight overlap in tool engagement distance (approximately 0.2mm). This technique serves to circumvent potential inaccuracies in the machine’s lead screw precision.
While this strategy effectively prevents the formation of tool marks, it causes an element of repetitive machining when the material of the product is a soft metal. Consequently, this section may exhibit variations in texture and color compared to other areas.
Fish Scale Patterns on Flat Machined Surfaces
Causes: Fish scale or circular patterns appearing on the product’s flat surfaces. The cutting tools used for processing soft metals such as aluminum/copper are generally alloy material mills with 3 to 4 flutes. They have a hardness ranging from HRC55 to HRC65. These milling cutting tools are performed using the bottom edge of the tool, and the part surface may develop distinctive fish scale patterns, impacting its overall appearance.
Solution: Commonly observed in products with high flatness requirements and flat surfaces featuring recessed structures. A remedy is to switch to cutting tools made from synthetic diamond material, which helps achieve smoother surface finishes.
Aging and Wear of Equipment Components
Causes: The tools mark on the product surface is attributed to the aging and wear of the equipment’s spindle, bearings, and lead screw. Additionally, inadequate CNC system backlash parameters contribute to pronounced tool marks, particularly when machining rounded corners.
Solution: These issues stem from equipment-related factors and can be addressed by targeted maintenance and replacement.
결론
Achieving an ideal surface in the CNC machining metals demands useful approaches. There are different methods to avoid tool marks and lines that involve a combination of equipment maintenance, fixture enhancements, process adjustments, and programming refinements. By understanding and rectifying these factors, manufacturers can ensure that precision components not only meet dimensional criteria but also exhibit the desired aesthetic qualities.
권장 사항
스텝 터닝과 테이퍼 터닝: 차이점은 무엇인가요?
선삭은 수세기 동안 제조 산업을 지탱해 온 기본적인 가공 작업입니다. 터닝은 계속해서 진화하고 있으며 오늘날까지도 핵심 제조 기술입니다. 이 기사에서는 선삭 가공의 두 가지 유형인 스텝 선삭과 테이퍼 선삭에 대해 설명합니다. 선삭은 기본적으로 날카로운 절삭 공구가 표면에서 재료를 제거하여 회전하는 공작물을 형성하는 절삭 작업으로, 스텝 공정과 테이퍼 선삭 공정을 살펴보고 그 차이점을 설명합니다.
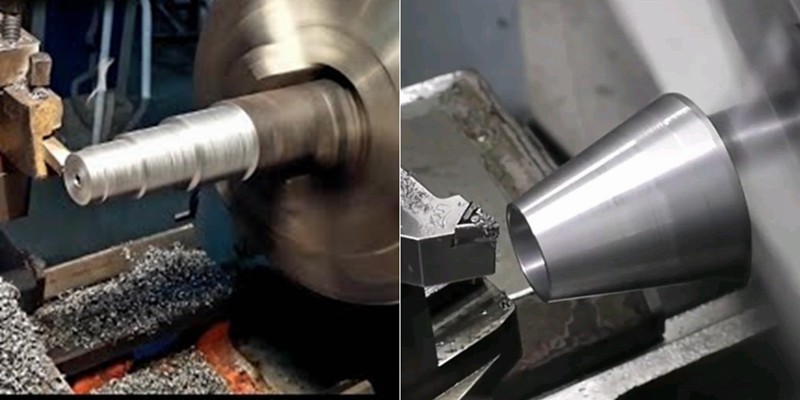

4축 CNC 기계를 작동할 때 로터리의 회전 중심을 결정하는 방법은 무엇입니까?
오늘날 4축 로터리 테이블은 기계 공장에서 흔히 볼 수 있는 장비입니다. 하나의 좌표에서 여러 면의 가공을 완료하려면 프로그래밍 좌표가 로터리 테이블의 좌표와 동기화되어야 합니다. 이 기사에서는 4축 로터리 테이블의 회전 중심을 결정하는 방법을 공유하겠습니다.여기서는 공작 기계의 X축을 중심으로 회전하는 4축 로터리 테이블을 보여주며, 여기서 회전 축을 A축이라고 합니다. 한마디로...
SFM이란? 가공 시 분당 표면 피트에 대한 완벽한 가이드
SFM, meaning Surface Feet per Minute in CNC machining, measures how fast a cutting tool moves across a workpiece. It is expressed in feet per minute. SFM combines the tool or workpiece diameter with the spindle speed (RPM). A larger diameter or higher RPM results in a higher SFM. Machinists use surface feet per minute to determine the best cutting speed for a material. Different materials have recommended SFM values for optimal performance. For example, 303 annealed stainless steel has an...

Cost Of CNC Machining: What Affects & How to Save It?
CNC machining is a technique used to make precision parts and replicate amazing designs. There are a lot of advantages of CNC machining, such as increasing the speed of parts production. It also reduces human errors during manufacturing as it is being controlled by the computer. However, many people do not seem to understand the rationale behind its cost. The machine and material you use can affect the price. Today, many customers still struggle with CNC machining cost calculation. With t...

 심천 워싱 기술 유한공사
심천 워싱 기술 유한공사