建議
CNC Acrylic Machining: All You Need To Know Machined Acrylic Parts
Today we are going to look at the manufacturing processes of acrylic polymer or optical prototyping. It is one of the most widespread plastics all over the world and a prominent competitor to glass and polycarbonate. Due to the fact that acrylic parts are used in a lot of industry areas, it seems a good idea to look into its manufacturing processes, specifically CNC acrylic machining since that is the process that is present in almost any kind of acrylic production. In this article, we wi...
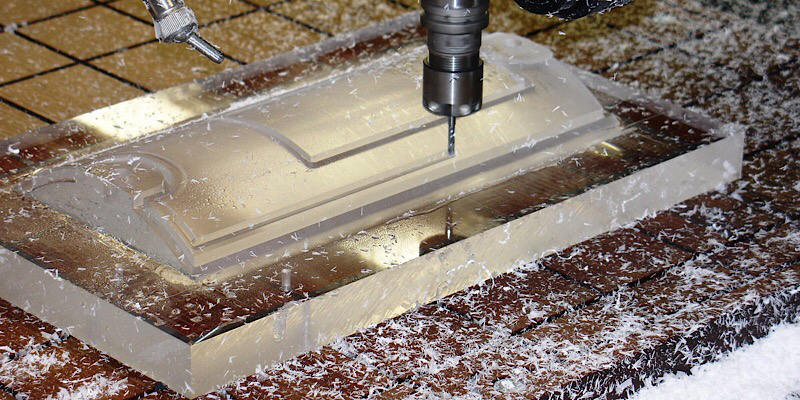

加工允許額解說:其計算方式及注意事項
加工余量是製造業的基本概念。它是 CNC 精密加工中常見的工程實務,可確保尺寸精度、表面品質,並生產可靠的功能性零件,適用於航空、國防和醫療等各種產業。本文嘗試回答這個問題:什麼是加工余量?我們將深入探討加工余量的概念,並討論為什麼機械師會留下加工余量?
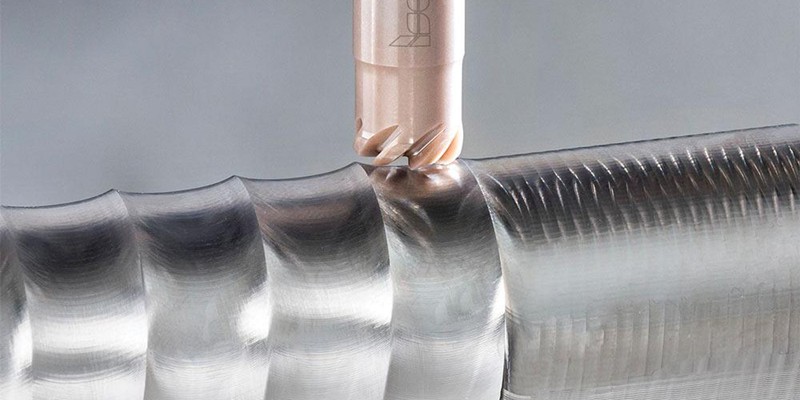

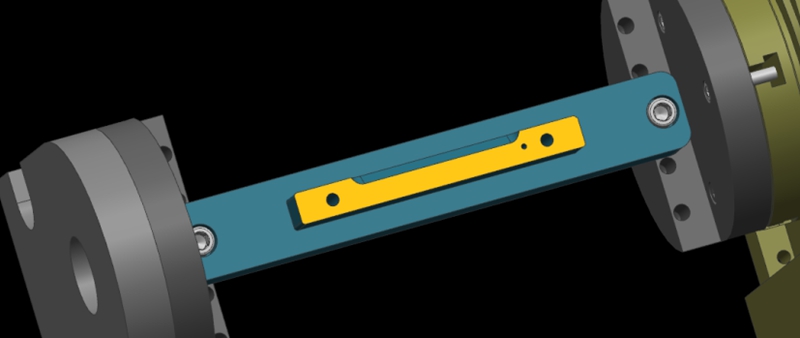
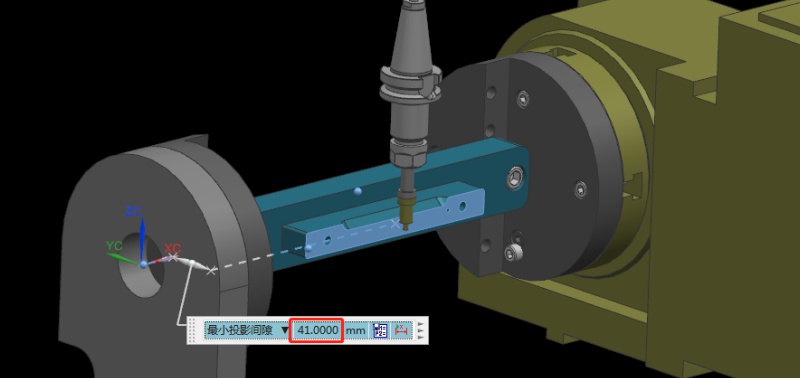
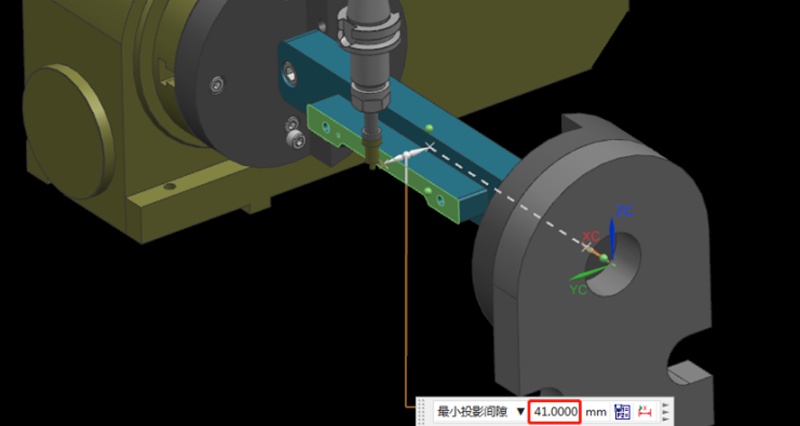
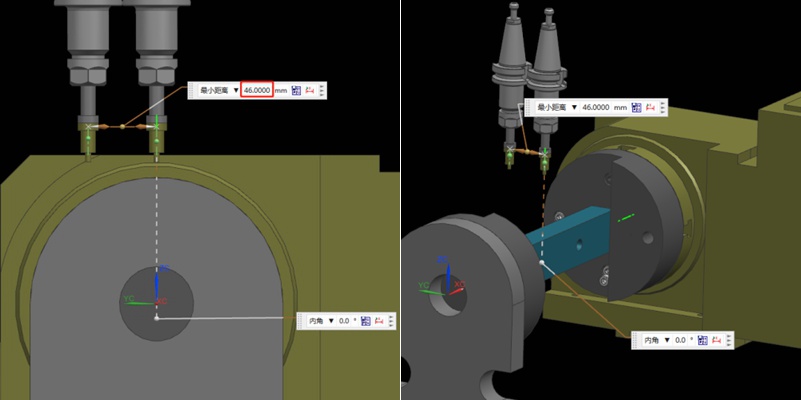
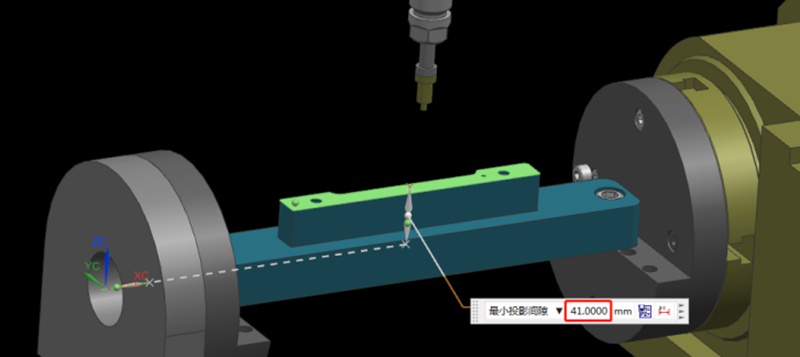
如何透過設計製程路徑和夾具來加工多面體鋁合金零件?
在加工製造領域中,選擇適當的加工策略對於提高生產效率非常重要。一般而言,多面體加工零件具有複雜的幾何形狀和嚴格的公差要求。因此,如何選擇合適的加工路徑加工這類零件,需要綜合考慮。在這篇文章中,Washxing 分析了多面體鋁合金零件的不同加工路徑,並比較了 3+2 軸 CNC 加工與 3+2 軸 CNC 加工的優劣。
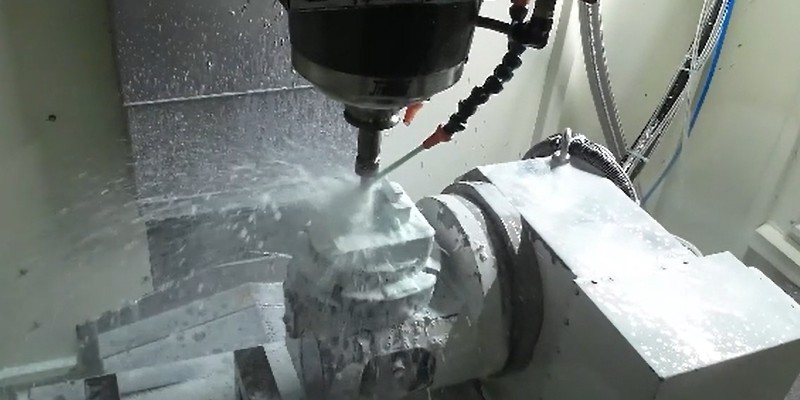

How To Create A Prototype With Steps: An Expert Guide
A prototype is an early version or physical model of a product idea that manufacturers can test and refine before investing in mass production. It acts as a product template and provides a practical approach to understanding a product’s appearance and function before production. When developing a product, product teams create a product prototype to test the product’s usability, design, and performance, gather user feedback, identify potential issues in the early stages, and identify possib...

 深圳市洗星科技有限公司
深圳市洗星科技有限公司