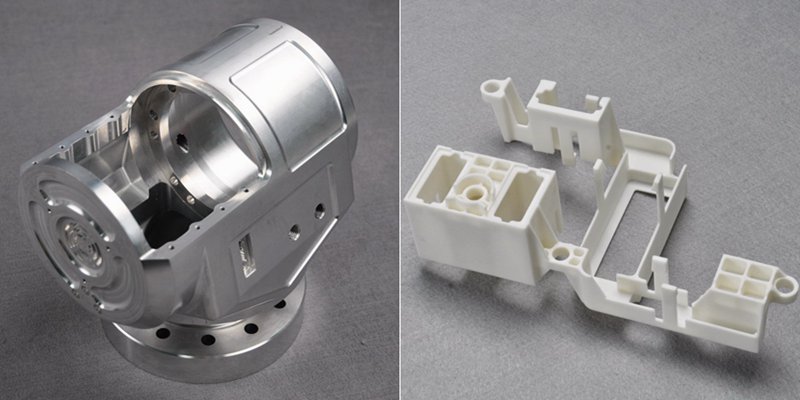
Wie bearbeitet man polyedrische Aluminiumteile durch die Entwicklung von Prozessrouten und Vorrichtungen?
Empfehlungen
Presssitz-Toleranz: Definition, Praktiken und Berechnung
Die verarbeitende Industrie ist sehr präzisionsorientiert, und selbst geringste Abweichungen können zu großen Unterschieden in der Produktqualität, den Kosten und dem Nutzen führen. Dieser Artikel befasst sich mit dem Thema Presspassung, bei der wenige Mikrometer Abweichung das Kriterium für das Versagen eines Teils sind. Wir erklären, was Presspassung ist, welche Faktoren die Presspassungstoleranz beeinflussen, und stellen ein Beispiel für einen Presspassungsrechner vor. Außerdem geben wir Ihnen einige wichtige Tipps, die Sie bei der Konstruktion von Bauteilen für die Presspassung...

CNC-Bearbeitung - Entwurf für die Fertigung: Technischer Leitfaden für Experten
Efficient CNC design is key to balancing functionality, cost, and production efficiency. By following these guidelines, you can avoid common design challenges, improve manufacturability, and streamline the production process. From minimizing thin walls and deep cavities to setting reasonable tolerances, each recommendation in this solution helps simplify machining while ensuring quality. Let’s get to it!The depth of cavities and grooves is typically limited by the cutting tool diameter us...
Wie vermeidet man Maschinenkollisionen während des Bearbeitungsprozesses?
Machine collision has always been an inevitable challenge in prototype and part machining. Operator errors, such as failing to perform tool settings, can lead to crashes. It will result in broken tools, scrapped workpieces, and reordering and reprocessing materials. In addition, without the automatic tool setter, manual tool setting when entering Z-value data error can also cause machine collision. In this article, we will share our summarized experiences to help you avoid this issue. Bef...

Produktion und Herstellung von Brücken: Wichtige Etappen und Vorteile
Adopting a final production process often involves numerous trials and failures, particularly during prototyping or low-volume production. Companies may temporarily select a production method until they are confident in their approach. Bridge production refers to this temporary strategy, enabling continued operations while a more reliable manufacturing process is developed. Understanding bridge production is crucial for enhancing product development and expediting operations. This article...

 ShenZhen Washxing Technology Co.,Ltd
ShenZhen Washxing Technology Co.,Ltd



