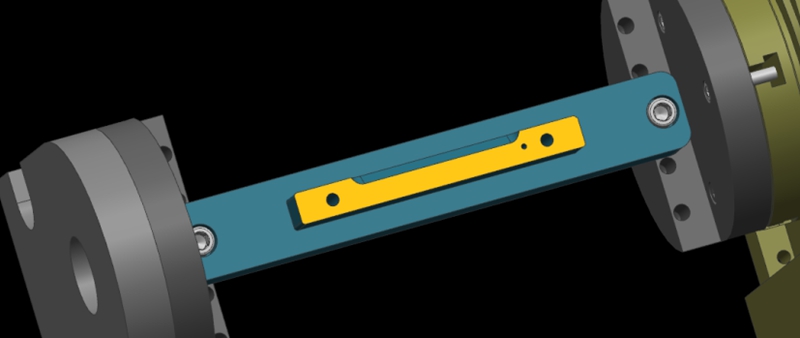
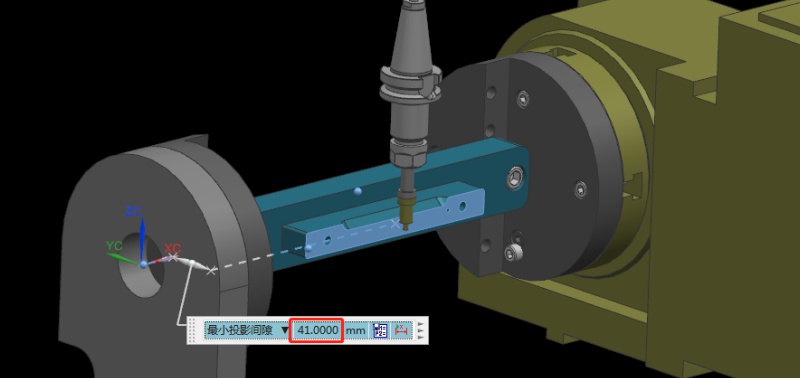
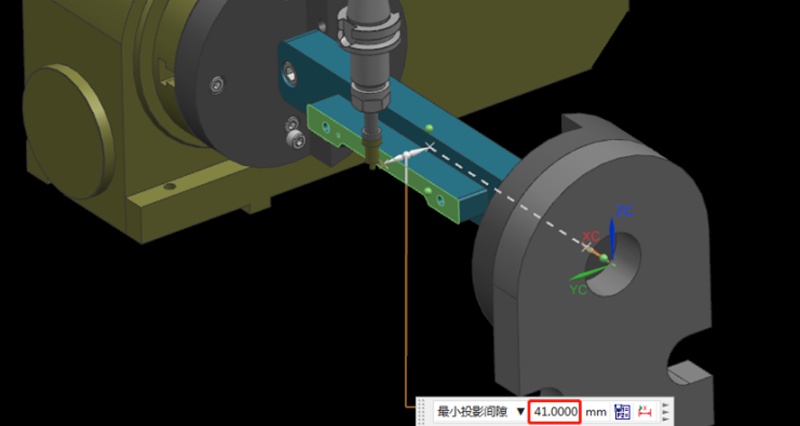
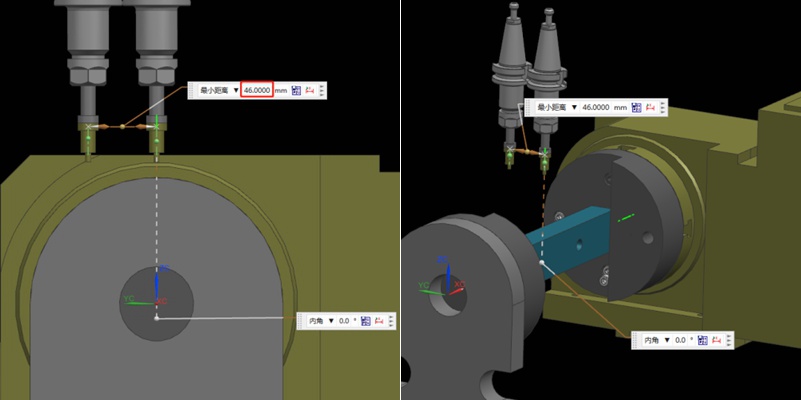
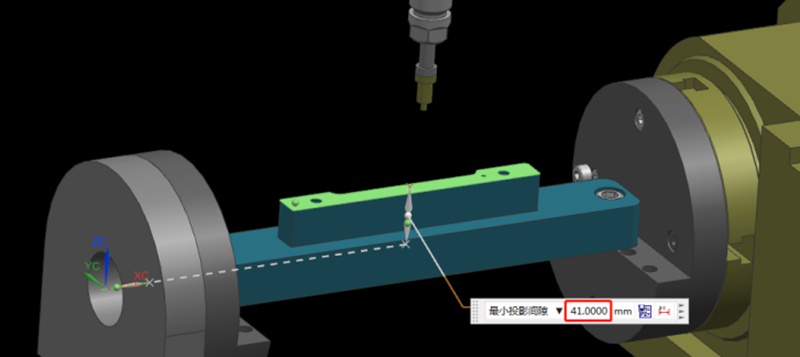
¿Cómo determinar el centro de rotación de rotación al operar una máquina CNC de 4 ejes?
Recomendaciones
Causas y soluciones de las marcas de herramientas en el mecanizado de metales
Las piezas metálicas de precisión suelen fabricarse utilizando diversas tecnologías de mecanizado de precisión, siendo el mecanizado CNC un método habitual. Por lo general, las piezas de precisión suelen exigir altos estándares tanto en dimensiones como en aspecto. Por lo tanto, cuando se utilizan metales de mecanizado CNC como el aluminio y el cobre, la aparición de marcas de herramientas y líneas en la superficie del producto acabado es motivo de preocupación. En este artículo se analizan las razones que provocan marcas y líneas de herramienta durante el mecanizado de productos metálicos....
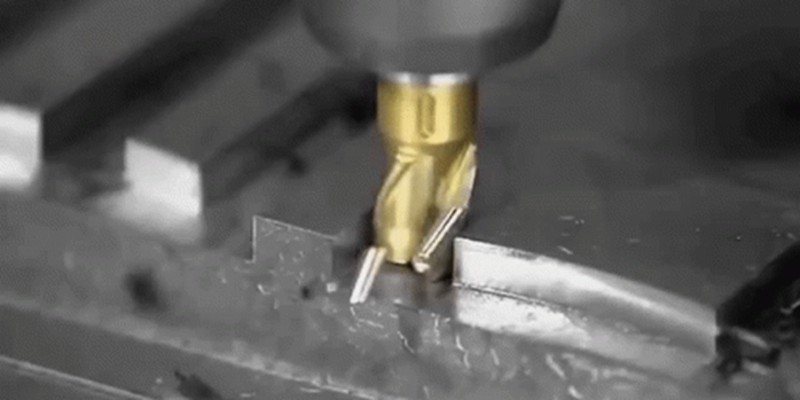

Explicación de la indemnización por mecanizado: Su cálculo y su importancia
Machining allowance is a fundamental concept in manufacturing. It is a common engineering practice in CNC precision machining, ensuring dimensional accuracy, surface quality, and the production of reliable and functional components for a range of industries, including aerospace, defense, and medical. This article attempts to answer the question: what is machining allowance? We will take a deep dive into the concept of machining allowance and discuss why machinists leave machining allowanc...

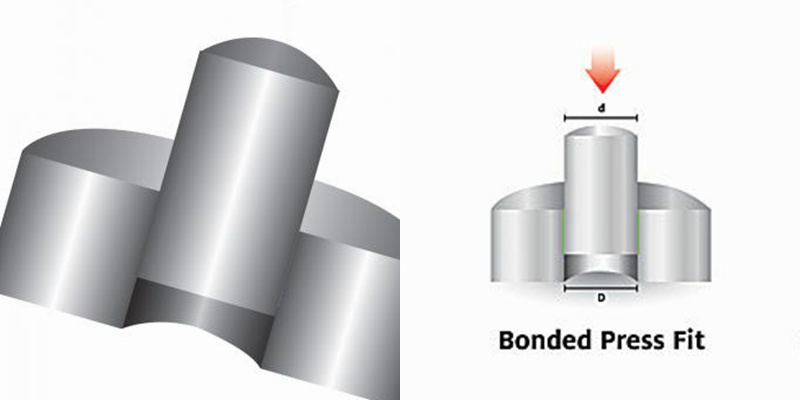
Press Fit Tolerance: Defination, Practices, And Calculation
The manufacturing industry is highly precision-centric, where even the slightest of margins can create huge differences in product quality, cost, and utility. This article discusses the topic of press fitting, where a few micrometers of deviation dictates the criterion for part failure. So, what is press fit and, the factors influencing press fit tolerancing, and present an example of a press fit calculator. We will also share some key tips to keep in mind while designing components for p...

Press Fit Tolerance: Defination, Practices, And Calculation
The manufacturing industry is highly precision-centric, where even the slightest of margins can create huge differences in product quality, cost, and utility. This article discusses the topic of press fitting, where a few micrometers of deviation dictates the criterion for part failure. So, what is press fit and, the factors influencing press fit tolerancing, and present an example of a press fit calculator. We will also share some key tips to keep in mind while designing components for p...
 ShenZhen Washxing Technology Co.,Ltd
ShenZhen Washxing Technology Co.,Ltd