Wie vermeidet man Maschinenkollisionen während des Bearbeitungsprozesses?
Empfehlungen
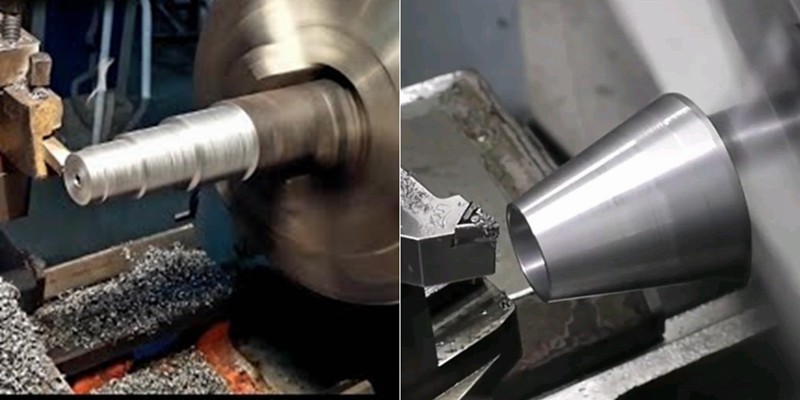
Stufendrehen vs. Kegeldrehen: Was sind die Unterschiede?
Turning is a fundamental machining operation that has supported the manufacturing industry for centuries. It continues to evolve and is a core manufacturing technique to this day. This article will discuss two types of turning operations: step turning vs taper turning. We will explore the step process and taper turning process and explain their differences.Turning is essentially a cutting operation where a sharp cutting tool shapes a rotating workpiece by removing material from its surfa...

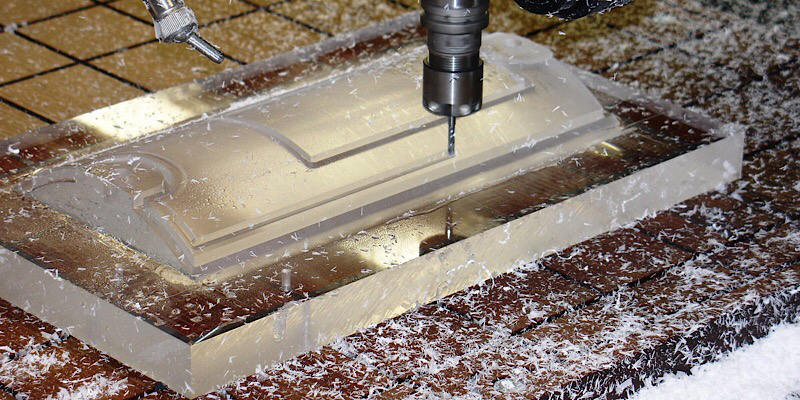
CNC Acrylic Machining: All You Need To Know Machined Acrylic Parts
Today we are going to look at the manufacturing processes of acrylic polymer or optical prototyping. It is one of the most widespread plastics all over the world and a prominent competitor to glass and polycarbonate. Due to the fact that acrylic parts are used in a lot of industry areas, it seems a good idea to look into its manufacturing processes, specifically CNC acrylic machining since that is the process that is present in almost any kind of acrylic production. In this article, we wi...

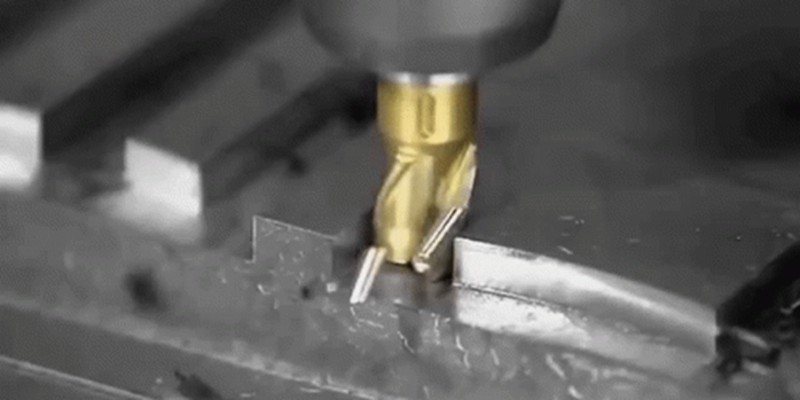
Ursachen und Lösungen für Werkzeugabdrücke bei der Bearbeitung von Metall
Precision metal parts are often manufactured using various precision machining technologies, with CNC machining being a common method. Usually, precision parts typically demand high standards for both dimensions and appearance. Therefore, when using CNC machining metals such as aluminum and copper, the occurrence of tool marks and lines on the finished product’s surface is a concern. This article discusses the reasons that cause tool marks and lines during the machining of metal products....

CNC-Bearbeitung - Entwurf für die Fertigung: Technischer Leitfaden für Experten
Efficient CNC design is key to balancing functionality, cost, and production efficiency. By following these guidelines, you can avoid common design challenges, improve manufacturability, and streamline the production process. From minimizing thin walls and deep cavities to setting reasonable tolerances, each recommendation in this solution helps simplify machining while ensuring quality. Let’s get to it!The depth of cavities and grooves is typically limited by the cutting tool diameter us...
 ShenZhen Washxing Technology Co.,Ltd
ShenZhen Washxing Technology Co.,Ltd


