권장 사항
CNC 아크릴 가공: 가공된 아크릴 부품에 대해 알아야 할 모든 것
오늘은 아크릴 폴리머 또는 광학 프로토타이핑의 제조 공정에 대해 살펴보겠습니다. 아크릴은 전 세계적으로 가장 널리 사용되는 플라스틱 중 하나이며 유리와 폴리카보네이트의 유력한 경쟁자입니다. 아크릴 부품은 많은 산업 분야에서 사용되기 때문에 거의 모든 종류의 아크릴 생산에 존재하는 공정이기 때문에 제조 공정, 특히 CNC 아크릴 가공을 살펴보는 것이 좋습니다. 이 기사에서 우리는 ...

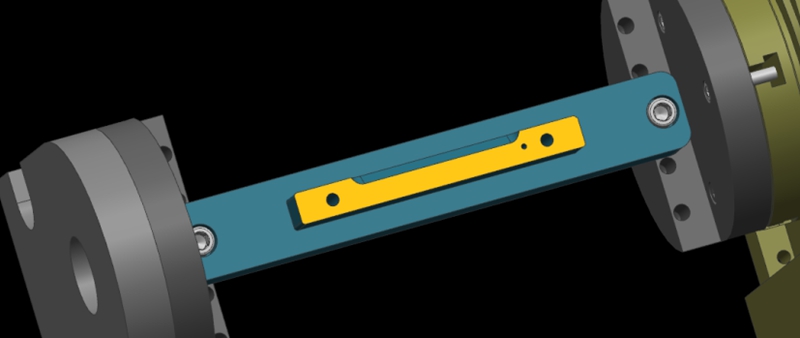
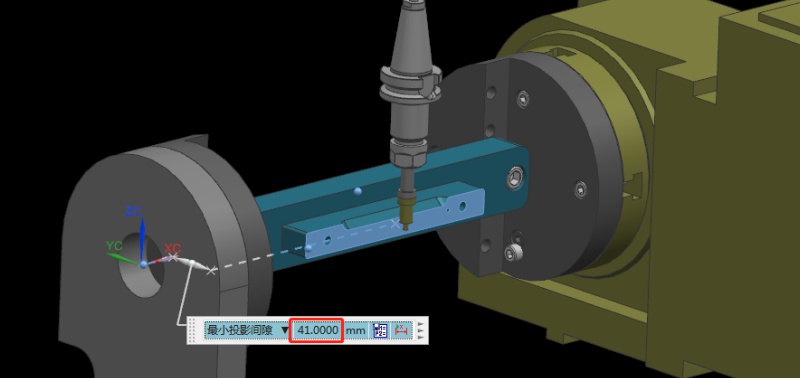
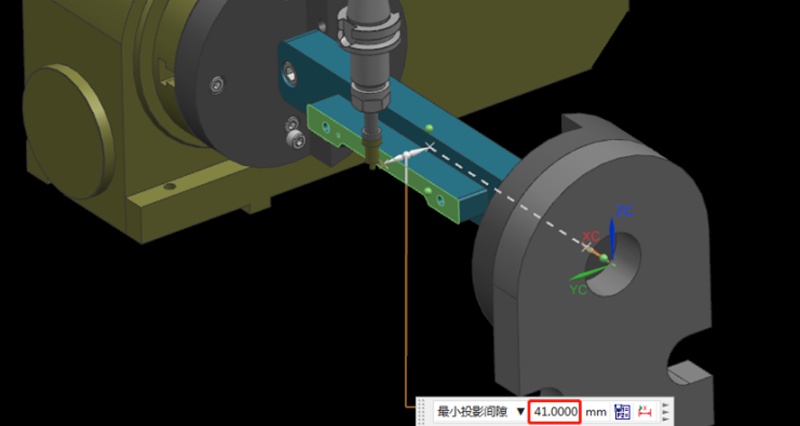
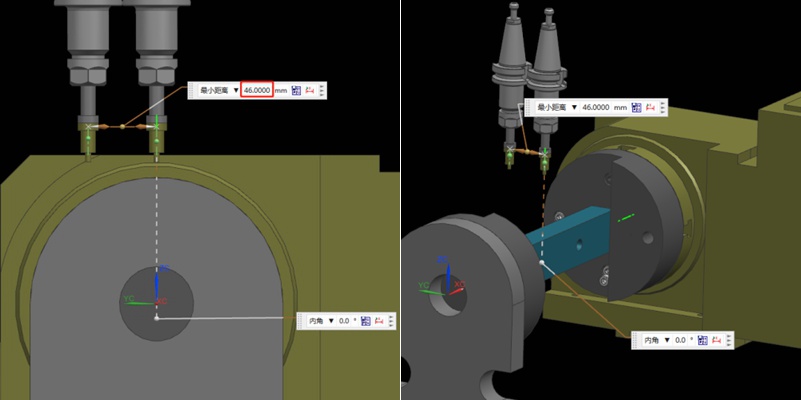
가공 공정에서 기계 충돌을 피하는 방법은?
기계 충돌은 프로토타입 및 부품 가공에서 항상 피할 수 없는 과제였습니다. 공구 설정 실패와 같은 작업자 오류는 충돌로 이어질 수 있습니다. 이는 공구 파손, 공작물 폐기, 재료 재주문 및 재가공으로 이어질 수 있습니다. 또한 자동 공구 세터가 없는 경우 Z값 데이터 오류 입력 시 수동 공구 설정도 기계 충돌을 일으킬 수 있습니다. 이 기사에서는 이러한 문제를 방지하는 데 도움이 되는 요약된 경험을 공유합니다. Bef...

SFM이란? 가공 시 분당 표면 피트에 대한 완벽한 가이드
SFM, meaning Surface Feet per Minute in CNC machining, measures how fast a cutting tool moves across a workpiece. It is expressed in feet per minute. SFM combines the tool or workpiece diameter with the spindle speed (RPM). A larger diameter or higher RPM results in a higher SFM. Machinists use surface feet per minute to determine the best cutting speed for a material. Different materials have recommended SFM values for optimal performance. For example, 303 annealed stainless steel has an...

제조용 CNC 가공 설계: 전문가 기술 가이드
효율적인 CNC 설계는 기능, 비용, 생산 효율성의 균형을 맞추는 데 핵심입니다. 이 가이드라인을 따르면 일반적인 설계 문제를 방지하고 제조 가능성을 개선하며 생산 프로세스를 간소화할 수 있습니다. 얇은 벽과 깊은 캐비티 최소화부터 합리적인 공차 설정까지, 이 솔루션의 각 권장 사항은 가공을 간소화하는 동시에 품질을 보장하는 데 도움이 됩니다. 시작하겠습니다! 캐비티와 홈의 깊이는 일반적으로 절삭 공구 직경에 의해 제한됩니다...
 심천 워싱 기술 유한공사
심천 워싱 기술 유한공사